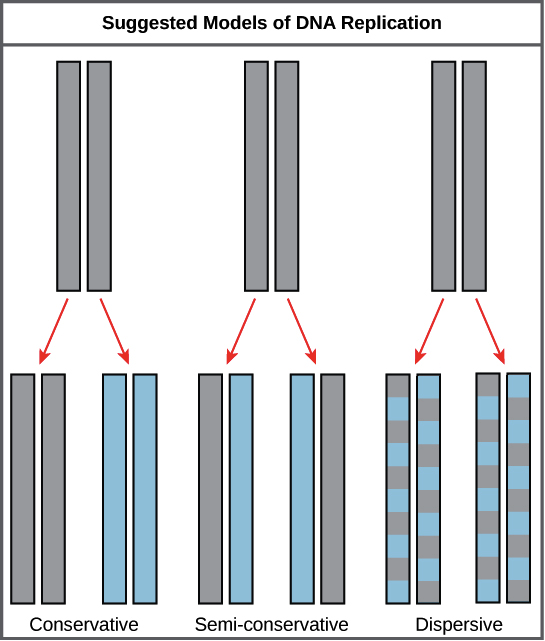
Semi-Conservative Conservative Dispersive models of DNA replication. Each strand of the DNA has the ability to form a new.

Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry
All of these are hard for a teacher to describe without having a visible model or.

. Multiple replication sites on DNA model. Watson and Crick proposed a Semi-Conservative model for DNA replication in 1953 which derived from their model of the DNA double helix. There were three models which were initially formed for the replication process of DNA.
Central dogma explains how the DNA makes its own copies through DNA replication which then codes for the RNA in transcription and further RNA codes for the proteins by the translation. Define terms related to step 3 Origin of replication Helicase Single strand binding. Initiator binding i facilitates replicative helicase loading ii onto duplex DNA to license origins.
DNA replication is the production of identical DNA helices from a single double-stranded DNA molecule. Literally replication means the process of duplication. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings.
The semi- conservative model of DNA explains that the two strands of DNA separate for replication much like a zipper. Out of these the semi- conservative model of DNA replication is the most widely accepted one. In this proposal the strands of the duplex separate and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand.
Strand that needs to wait until more opens then put a primer on and run 5 to 3 then go backward and put on another primer and run 5 to 3 primer follows replication fork but replicates the other way. These are briefly discussed as follows. DNA replication is a process that all cells must go through prior to any type of cell division.
When cells replicate their DNA they make two identical copies of their DNA from the original copy. Three Different Models for DNA Replication. Although I think that this way was a very good way of modeling DNA replication there are other alternatives for modeling DNA replicationa s well.
In the replication factory model after both DNA helicases for leading strands and lagging strands are loaded on the template DNAs the helicases run along the DNAs into each other. Adds new nucleotides to both DNA template strands. On your own using your half as a pattern add new nucleotides to the original half of the model.
After replication the single daughter molecules contain a strand of the original parent molecule and a new strand. Describe an alternative way of modeling DNA replication. Up to 24 cash back Separate your DNA model along the points of attachment between base pairs.
Each molecule consists of a strand from the original molecule and a newly formed strand. In an alternative figure DNA factories are similar to projectors and DNAs are like as cinematic films passing constantly into the projectors. The Dispersive Model describes the original DNA breaking apart and the newly.
STEP ONE What enzyme found in DNA is responsible for breaking the hydrogen bonds linking base pairs together. For example maybe with different materials such as candy or. DNA is a twisted double helix.
Gray indicates the original DNA strands and blue indicates newly. The small pieces of the lagging strand. Opens unwinds the double-stranded DNA.
This will separate the two ladder halves. Initially the simplest mechanism of DNA replication seemed to be the continuous growth of both new strands nucleotide by nucleotide at the replication fork as it moves from one end of a DNA molecule to the other. Helicase enzyme breaks hydrogen bonds between bases unzips and unwinds the helix A protein that catalyzes chemical.
List three ways RNA is different than DNA. Synthesizes short RNA sequences known as primers which are required to start DNA replication. Twist the joined strands into a helix and then let it go.
RNA Primase Primer DNA. Watson and Crick had proposed that in order to copy itself DNA would have to open down the center sort of. Iii A subset of loaded helicases is activated for replisome assembly.
Cairns model of DNA Replication. In the semi-conservative model the two parental strands separate and each makes a copy of itself. DNA replication in 7 easy steps.
The Steps of DNA Replication 1. The Semi-Conservative Model describes the double stranded DNA molecule separating and each strand replicates. Prior to replication the DNA uncoils and strands separate.
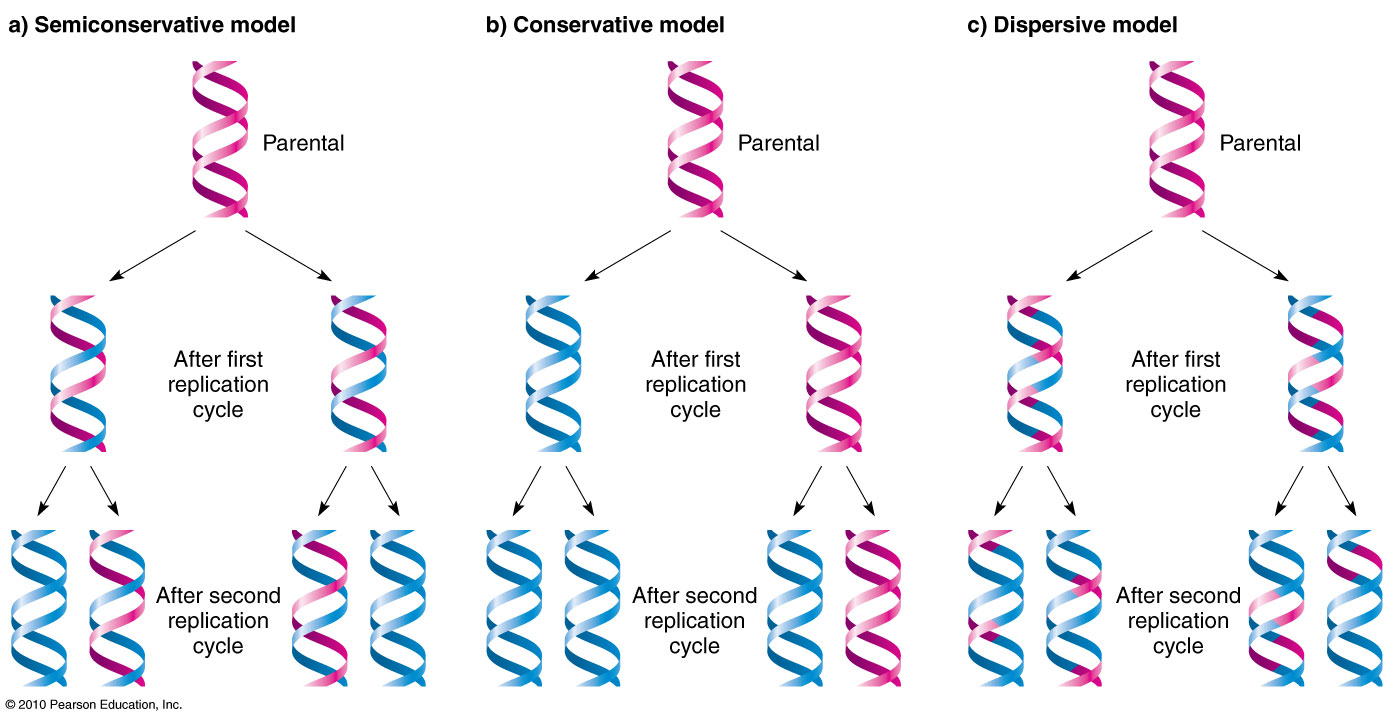
Replication proceeds bidirectionally from origins and terminates when replication forks from adjacent active origins meet iv. Start with the two 30-inch white VelcroTM strands joined together. Note that after two rounds two of the DNA molecules consist only of new material while the.
Presence of all four types of nucleotide both strands of the DNA they act as a template DNA polymerase an enzyme a source of energy. This model for replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied Figure 2. But because of the antiparallel orientation of the two DNA strands in the DNA double helix see Figure 5-2 this mechanism would require one daughter strand to.
1 Cairns Model and 2 Rolling circle model. The semiconservative model of DNA replication is shown. In this work we are modeling intermediates representing the DNA core of the replication structures present at one arm of the replication fork.
A replication fork is formed which serves as a template for replication. Regarding DNA replication students can observe DNA synthesis direction the concepts of leading and lagging strands and the semiconservative nature of the whole process. It has long been proposed that slippage mechanisms are responsible for frameshill mutations such as double base -2 deletions during replication of DNA 123.
What are the four things that are required for semi-conservative replication to take place. After one round of replication the two daughter molecules each comprises one old and one new strand. 100 3 ratings 1.
In conclusion DNA replication is the mechanism by which a cell unwinds the DNA double helix and duplicates both. Be used in this demonstration to show the steps of DNA replication. This model of DNA replication in prokaryotes was proposed by Cairns in 1963It explains the mechanism of DNA replication in double stranded circular DNA of bacteria.
There are two most commonly known models of circular DNA replication viz. One partner gets the left half of the ladder and the other partner gets the right half. In molecular biology DNA replication is the primary stage of inheritance.
Compare the life cycles of RNA and DNA viruses.
Mode Of Dna Replication Meselson Stahl Experiment Article Khan Academy

0 Comments